Key-Value - Chained
In this example we will show how we can create a service whose source and sink are both key-value.
Prerequisites
This guide uses local Fluvio cluster. If you need to install it, please follow the instructions at here.
Dataflow
Overview
For this example, we will write a dataflow that tracks the manufacture location of a car based on the VIN number. The source is key-value whose key is the vin and the value is the car info. The sink's key is the manufacture location and the value is an object with the old key.
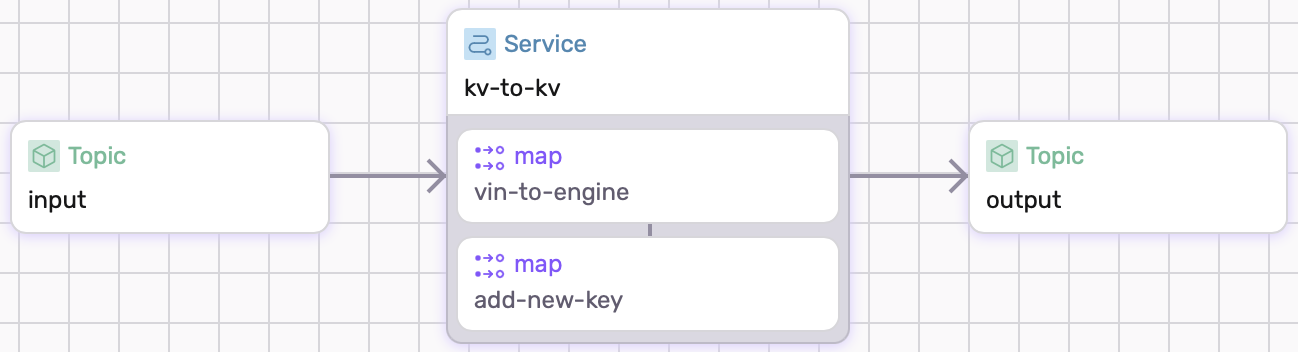
Define the types
Like the previous example, we will need to define our types.
types:
car-info:
type: object
properties:
year:
type: u32
brand:
type: string
model:
type: string
car-short:
type: object
properties:
vin:
type: string
desc:
type: string
car-info
This object is for the source's value.
car-short
This object is for the sinks's value. The vin is the key from the sink.
Topic List
The following is our list of topics. Both are key-value.
topics:
input:
schema:
key:
type: string
value:
type: car-info
output:
schema:
key:
type: string
value:
type: car-short
Transform
We will apply two map tranforms.
transforms:
- operator: map
run: |
fn vin_to_car(vin: Option<String>, car: CarInfo) -> Result<CarShort> {
Ok(CarShort{
vin: vin.unwrap(),
desc: format!("{} {} {}",car.year,car.brand,car.model),
})
}
- operator: map
run: |
fn car_to_manu(vin: Option<String>, car_short: CarShort) -> Result<(Option<String>, CarShort)> {
let country = if let Some(first_char) = vin.unwrap().chars().next() {
if first_char == '1' || first_char == '4' || first_char == '5' { "United States" }
else if first_char == '2' { "Canada" }
else if first_char == '3' { "Mexico" }
else if first_char == 'J' { "Japan" }
else if first_char == 'K' { "South Korea" }
else if first_char == 'L' { "China" }
else if first_char == 'S' { "United Kingdom" }
else if first_char == 'V' { "France" }
else if first_char == 'W' { "Germany" }
else if first_char == 'Z' { "Italy" }
else { "Unknown" }
}
else { "Invalid VIN" };
Ok((Some(country.to_string()), car_short))
}
vin-to-car() creates the value for the sink and car_to_manu modifies the key for the sink.
Running the Example
Full Code
Copy and paste following config and save it as dataflow.yaml.
apiVersion: 0.5.0
meta:
name: chained-key
version: 0.1.0
namespace: example
config:
converter: json
consumer:
default_starting_offset:
value: 0
position: End
types:
car-info:
type: object
properties:
year:
type: u32
brand:
type: string
model:
type: string
car-short:
type: object
properties:
vin:
type: string
desc:
type: string
#Both topics are key-values
topics:
input:
schema:
key:
type: string
value:
type: car-info
output:
schema:
key:
type: string
value:
type: car-short
services:
kv-to-kv:
sources:
- type: topic
id: input
transforms:
- operator: map
run: |
fn vin_to_car(vin: Option<String>, car: CarInfo) -> Result<CarShort> {
Ok(CarShort{
vin: vin.unwrap(),
desc: format!("{} {} {}",car.year,car.brand,car.model),
})
}
- operator: map
run: |
fn car_to_manu(vin: Option<String>, car_short: CarShort) -> Result<(Option<String>, CarShort)> {
let country = if let Some(first_char) = vin.unwrap().chars().next() {
if first_char == '1' || first_char == '4' || first_char == '5' { "United States" }
else if first_char == '2' { "Canada" }
else if first_char == '3' { "Mexico" }
else if first_char == 'J' { "Japan" }
else if first_char == 'K' { "South Korea" }
else if first_char == 'L' { "China" }
else if first_char == 'S' { "United Kingdom" }
else if first_char == 'V' { "France" }
else if first_char == 'W' { "Germany" }
else if first_char == 'Z' { "Italy" }
else { "Unknown" }
}
else { "Invalid VIN" };
Ok((Some(country.to_string()), car_short))
}
sinks:
- type: topic
id: output
Running SDF
To run example:
$ sdf run
Produce data
We will produce some data by writing it into a file name cars.txt.
WBA7B41090G123456>{"year":1995,"brand":"BMW","model":"740i"}
1HGCB765XMA000001>{"year":1991,"brand":"Honda","model":"Accord"}
JM1FD3319P0112345>{"year":1991,"brand":"Mazda","model":"RX-7"}
KMHDH41D48U123456>{"year":2008,"brand":"Hyundai","model":"Elantra"}
JHMCB7658KC123456>{"year":1989,"brand":"Honda","model":"Accord"}
ZFA3120000S123456>{"year":2015,"brand":"Fiat","model": "500"}
We can produce data via
$ fluvio produce input --key-separator ">" -f cars.txt
$ fluvio consume input -Bdk
Consume data
To consume the data
$ fluvio consume output -Bdk
[Germany] {"desc":"1995 BMW 740i","vin":"WBA7B41090G123456"}
[United States] {"desc":"1991 Honda Accord","vin":"1HGCB765XMA000001"}
[Japan] {"desc":"1991 Mazda RX-7","vin":"JM1FD3319P0112345"}
[South Korea] {"desc":"2008 Hyundai Elantra","vin":"KMHDH41D48U123456"}
[Japan] {"desc":"1989 Honda Accord","vin":"JHMCB7658KC123456"}
[Italy] {"desc":"2015 Fiat 500","vin":"ZFA3120000S123456"}
The output's key is the country of the manufacture for the car and the value is the new object generated from the vin_to_car() function.
Cleanup
Exit sdf terminal and clean-up. The --force flag removes the topics:
$ sdf clean --force
Conclusion
This how-to focused on using key-values as output as well as the input. The following pages contains another example of key-value as chained.